How about we get into the genuine SEO tactics and strategies that will assist you with getting additional traffic from search engines.
Keyword Research & Keyword Targeting
The initial phase in search motor optimization is true to determine what it is you’re really streamlining for. This implies identifying the terms individuals are searching for (otherwise called “keywords”) that you believe your website should rank for in search engines like Google.
Sounds sufficiently straightforward, correct?
I need my widget organization to show up when individuals search for “widgets,” and perhaps when they type in things like “purchase widgets.” Onto stage three!
Tragically, it’s not exactly that straightforward. There are a couple of key factors to consider while determining the keywords you need to focus on your site:
Search Volume: The main factor to consider is the number of individuals (if any) who are really searching for a given catchphrase. The more individuals there are searching for a watchword, the greater the audience you stand to reach. Conversely, on the off chance that nobody is searching for a catchphrase, there is no audience accessible to track down your content through search.
Relevance – If a term is habitually searched for that is incredible: however, imagine a scenario where it’s not totally pertinent to your prospects.
Relevance appears to be direct right away: Assuming you’re selling enterprise email marketing automation software you don’t have any desire to appear for searches that don’t have a say in your business, similar to “pet supplies.” But what might be said about terms like “email marketing software”?
This could naturally appear as though an extraordinary description of what you do, however assuming you’re offering to Fortune 100 organizations, the greater part of the traffic for this extremely competitive term will be searchers who don’t have any interest in purchasing your software (and the people you would like to reach could never purchase your expensive, complex solution based on a straightforward Google search).
Conversely, you could think a tangential watchword like “best enterprise PPC marketing solutions” is absolutely insignificant to your business since you don’t sell PPC marketing software. Be that as it may, assuming your possibility is a CMO or marketing chief, getting in front of them with a supportive asset on assessing pay-per-click tools could be an incredible “first touch” and a magnificent method for beginning a relationship with a planned purchaser.
Competition: As with any business opportunity, in SEO you need to consider the possible expenses and probability of progress. For SEO, this implies understanding the relative competition (and probability to rank) for explicit terms.
To start with, you really want to understand who your planned clients are and what they’re probably going to search for. On the off chance that you don’t already understand who your prospects are, pondering that is a decent spot to begin, for your business overall yet in addition for SEO.
From that point you need to understand:
- What sorts of things would they say they are keen on?
- What issues do they have?
- What sort of language do they use to describe the things that they do, the tools that they use, and so on.?
- Who else would they say they are purchasing things from (this implies your competitors, yet additionally could mean tangential, related tools for the email marketing organization, think other enterprise marketing tools)?
Once you’ve addressed these questions, you’ll have an underlying “seed list” of potential keywords and spaces to assist you with getting additional watchword ideas and to put a few search volume and competition metrics around.
You can observe a more comprehensive rundown of catchphrase tools underneath, however, the fundamental idea is that in this underlying advance, you’ll need to run various searches with a variety of various watchword tools.
You can likewise utilize competitive watchword tools like SEM Rush to see what terms your competitors are positioning for. These tools take a gander at a huge number of various search results and will show you each search term they’ve seen your rival positioning in Google recently.
Once more: this doesn’t simply need to be something you take a gander at for competitors. You could take a gander at related tools that are offering similar markets for content ideas, and even glance at the significant specialty distributers who talk about your subject (and that your prospects are reading) and see what sorts of keywords those locales are driving traffic for.
Additionally, assuming you have a current site, you’re probably getting some traffic from search engines already. Assuming that is the situation, you can utilize your very own portion of watchword information to assist you with understanding which terms are driving traffic (and which you could possibly rank a digit better for).
Tragically, Google has quit delivering a great deal of the information about the thing individuals are searching for to analytics providers, yet you can utilize SEM Rush (or comparable tools, like SpyFu) on your own site to get a feeling of the terms you’re positioning for and their assessed search volume.
Google likewise makes a smidgen a greater amount of this information accessible in their free Google Search Console interface (on the off chance that you haven’t set up a record, this is an entirely valuable SEO apparatus both for uncovering search questions information and for diagnosing various technical SEO issues.
Once Google Search Console is set up, you can explore this connect when signed in and see the search inquiries that are directing people to your site:
These could be great terms to concentrate additional content promotion and internal linking around (additional on every one of those subjects later), and could likewise be extraordinary “seed keywords” to assist you with getting more good thoughts about what to target.
Once you’ve invested in some opportunity to understand how your prospects to talk and what they search for, have taken a gander at the keywords directing people to your competitors and related locales, and have taken a gander at the terms directing people to your own site, you really want to attempt to understand which terms you might conceivably rank for and where the best opportunities truly lie.
On-Page Optimization
Once you have your watchword list, the subsequent stage is really implementing your designated keywords into your site’s content.
Each page on your site ought to focus on a center term and a “container” of related terms. In his outline of the perfectly improved page, Rand Fishkin offers a decent visual of what a well (or perfectly) advanced page resembles:
We should take a gander at a couple of basic, fundamental on-page elements you’ll need to understand as you ponder how to drive search motor traffic to your website:
1. Title Tags
While Google is attempting to more readily understand the genuine significance of a page and de-emphasizing (and, surprisingly, rebuffing) aggressive and manipulative utilization of keywords, including the term (and related terms) that you need to rank for in your pages is as yet valuable. Furthermore, the absolute most effective spot you can put your watchword is your page’s title tag.
The title tag isn’t your page’s essential headline. The headline you see on the page is commonly an H1 (or conceivably an H2) HTML component. The title tag is what you can see at the actual top of your browser, and is populated by your page’s source code in a meta tag:
The length of a title tag that Google will show will differ (it’s based on pixels, not character counts) yet overall 55-60 characters is a decent guideline here. If conceivable you have any desire to chip away at your center catchphrase, and in the event that you can do it in a characteristic and convincing manner, add a few related modifiers around that term too.
However, remember: the title tag will habitually be what a searcher finds in search results for your page. It’s the “headline” in organic search results, so you additionally need to consider how clickable your title tag is.
2. Meta Descriptions
While the title tag is successfully your search posting’s headline, the meta description (another meta HTML component that can be refreshed in your site’s code, yet isn’t seen on your real page) is actually your site’s additional ad copy.
Google mistreats what they show in search results, so your meta description may not consistently show, however assuming you have a convincing description of your page that would make people searching prone to click, you can incredibly increment traffic. (Keep in mind: appearing in search results is only the initial step! You actually need to get searchers to come to your site, and afterward, really make the move you need.)
Here is an illustration of a genuine world meta description displayed in search results:
3. Body Content
The genuine content of your page itself is, obviously, vital. Various kinds of pages will have unique “positions”, your cornerstone content resource that you believe bunches of people should connect to should be totally different than the help content that you need to ensure your clients find and find a solution rapidly.
All things considered, Google has been progressively leaning toward specific kinds of content, and as you work out any of the pages on your site, there are a couple of things to remember:
Thick and Unique Content – There is no enchanted number in terms of word count, and assuming that you have a couple of pages of content on your site with a modest bunch of two or three hundred words you won’t be dropping out of Google’s great graces, however, overall ongoing Panda refreshes specifically favor longer, unique content.
Assuming you have a huge number (think great many) of very short pages or loads of copied content where nothing changes except for the page’s title tag and say a line of text, that could cause you problems. Check out the whole of your site: are a huge percentage of your pages dainty, copied, and low worth?
Assuming this is the case, attempt to identify a way to “thicken” those pages, or check your analytics to perceive how much traffic they’re getting, and essentially exclude them (utilizing a No-Index meta tag) from search results to hold back from having it seem to Google that you’re attempting to flood their index with bunches of low-esteem pages trying to have them rank.
Engagement – Google is progressively weighting engagement and client experience metrics all the more vigorously. You can affect this by ensuring your content responds to the questions searchers are asking so that they’re probably going to remain on your page and draw in with your content. Ensure your pages load rapidly and don’t have design elements (like overly aggressive ads over the content) that would probably switch searchers off and send them away.
Sharability – Not each and every piece of content on your site will be connected to and shared many times. In any case, similarly, you need to be careful not to carry out huge amounts of pages that have meager content, you need to consider who might probably share and connect to new pages you’re making on your site before you carry them out.
Having huge amounts of pages that aren’t probably going to be shared or connected to doesn’t position those pages to rank well in search results, and doesn’t assist with making a decent image of your site overall for search engines, either.
4. Alt Attributes
How you increase your pictures can mean not just the way that search engines perceive your page yet in addition how much search traffic from the picture search your site generates. An alt attribute is an HTML component that permits you to provide alternative information for a picture in the event that a client can’t see it.
Your pictures might break over the long haul (documents get deleted, clients experience issues connecting to your site, and so forth) so having a valuable description of the picture can be useful from general ease of use perspective. This additionally offers you another chance, outside of your content, to assist searching engines in understanding what’s going on with your page.
You don’t have any desire to “catchphrase stuff” and pack your center watchword and each conceivable variation of it into your alt attribute. Truth be told, on the off chance that it doesn’t fit normally into the description, don’t include your objective catchphrase here by any stretch of the imagination.
Simply be certain not to skirt the alt attribute, and attempt to give an intensive, accurate description of the picture (envision you’re describing it to someone who can’t see it, that is the thing it’s there for!).
By expounding normally on your subject, you’re keeping away from “over-optimization” filters (in other words: it doesn’t make it seem as though you’re attempting to fool Google into positioning your page for your objective catchphrase) and you allow yourself a superior opportunity to rank for valuable modified “long tail” variations of your center point.
5. URL Structure
Your site’s URL structure can be significant both according to the following perspective (you can all the more effectively fragment information in reports utilizing a segmented, legitimate URL structure) and from a shareability standpoint (more limited, descriptive URLs are simpler to copy and glue and will quite often get erroneously cut off less often).
Once more: don’t attempt to pack in however many keywords as could be expected under the circumstances; make a short, descriptive URL.
Additionally: on the off chance that you don’t need to, don’t change your URLs. Regardless of whether your URLs aren’t “pretty” in the event that you don’t feel like they’re adversely affecting clients and your business, as a rule, don’t transform them to be more watchword-centered for “better SEO.”
If you truly do need to change your URL structure, make a point to utilize the proper (301 permanent) sort of redirect. This is common slip-up organizations make when they redesign their websites.
6. Schema & Markup
At long last, once you have all of the norm on-page elements dealt with, you can consider going above and beyond and better aiding Google (and other search engines, which likewise perceive schema) to understand your page.
Schema markup doesn’t make your page appear higher in search results (it’s anything but a positioning factor, at present). It gives your posting some additional “land” in the search results, the manner in which ad extensions accomplish for your Google Ads (previously known as AdWords) ads.
In some search results, if no other person is utilizing schema, you can help a pleasant advantage in click-through rate by the righteousness of the way that your site is showing things like evaluations while others don’t. In other search results, where everyone is utilizing schema, having audits might be “table stakes” and you may be harming your Google CTR by overlooking them:
There are a variety of various sorts of markup you can include on your site – most presumably won’t make a difference to your business, however, almost certainly, no less than one type of markup will apply to at minimum a portion of your site’s pages.
Information Architecture & Internal Linking
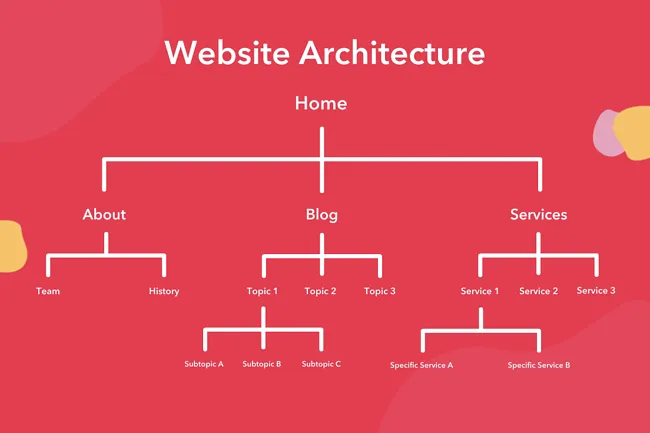
Information architecture refers to how you coordinate the pages on your website. The way that you put together your website and interlink between your pages can affect how various content on your webpage positions in response to searches.
The reason for this is that search engines generally perceive joins as “demonstrations of positive support” and a way to assist with understanding both what’s going on with a page, and how significant it is (and the way in which believed it ought to be).
Search engines likewise take a gander at the genuine text you use to connect to pages, called anchor text – utilizing descriptive text to connect to a page on your site assists Google with understanding what’s going on with that page (yet in a post-Penguin world particularly, be certain not to be overly aggressive in packing your keywords into linking text).
Similarly that a connection from CNN is an indication that your site could be significant assuming you are linking to a particular page aggressively from various regions on your site, that is an indication to search engines that that particular page is vital to your site.
Additionally: the pages on your site that have the most outer votes (joins from other, confided in destinations) have the most able to assist the other pages on your site with positioning in search results.
Content Marketing & Link Building
Since Google’s algorithm is still generally based on joins, having various great connects to your site is clearly inconceivably significant in driving search traffic: you can accomplish practically everything you need on-page and technical SEO, on the off chance that you don’t have connections to your site, you won’t appear in search results postings.
There are various ways of getting connections to your site, however as Google and other search engines become increasingly refined, a considerable lot of them have become incredibly dangerous (regardless of whether they might be in any casework for the time being).
Assuming you are new to SEO and are hoping to leverage the channel, these more dangerous and more aggressive methods for attempting to get connected likely are definitely not ideal for your business, as you won’t know how to properly explore the traps and assess the dangers.
Furthermore, attempting to make connections explicitly to control Google rankings makes no other incentive for your business if the search motor algorithms shift and your rankings vanish.
A more sustainable approach to developing connections is to zero in on more broad, sustainable marketing approaches, for example, making and promoting valuable content that likewise includes explicit terms you’d need to rank for and taking part in traditional PR for your business.
The most common way of making and promoting content that will get you connections and social offers is a labor-intensive one. Yet again you’ll track down more detailed bit by bit guides to various parts of content marketing beneath, and there are a variety of approaches to actually make content, assist it with getting found, and rank well in search results.
Common Technical SEO Issues
While fundamentals of SEO like the most effective methods for building connections to drive search motor rankings have changed as of late (and content marketing has become progressively significant) what many individuals would consider more “traditional SEO” is still amazingly valuable in creating traffic from search engines.
As we’ve already talked about, catchphrase research is as yet valuable, and technical SEO issues that hold Google and other search engines back from understanding and positioning locales’ content are as yet predominant.
Technical SEO for bigger, more muddled destinations is actually its own discipline, however, there are a few common mix-ups and issues that most locales face that considerably more modest to fair-sized organizations can profit from monitoring.
1. Page Speed
Search engines are putting a rising accentuation on having quick loading locales – the uplifting news is this isn’t only beneficial for search engines, yet in addition for your clients and your site’s conversion rates.
Google has really made a valuable device here to give you a few explicit suggestions on what to change on your site to address page speed issues.
2. Mobile Friendliness
Assuming your site is driving (or could be driving) critical search motor traffic from mobile searches, how “mobile-friendly” your site is will affect your rankings on mobile devices, which is a quickly developing section. In certain specialties, mobile traffic already offsets desktop traffic.
Google as of late declared an algorithm update zeroed in on this explicitly. Google offers an exceptionally accommodating free device to get recommendations on the best way to make your site more mobile-friendly.
3. Redirects
Improperly implementing redirects on your site can genuinely affect search results. Whenever you can stay away from it, you need to hold back from moving your site’s content starting with one URL then onto the next; in other words: assuming your content is on example.com/page, and that page is getting search motor traffic, you need to try not to move all of the content to example.com/different-url/newpage.html, except if there is a very strong business reason that would offset a potential present moment or even long-term misfortune in search motor traffic.
Assuming you really do have to move content, you need to ensure that you carry out permanent (or 301) redirects for content that is moving permanently, as brief (or 302) redirects (which are oftentimes utilized by developers) demonstrate to Google that the move may not be permanent and that they shouldn’t move all of the connection value and positioning capacity to the new URL. (Further, changing your URL structure could make broken joins, harming your referral traffic streams and making it hard for guests to explore your site.)
4. Duplicate Content
Slight and copied content is another area of accentuation with Google’s new Panda refreshes. By copying the content (putting something very similar or close to identical content on numerous pages), you’re weakening the connection value between two pages instead of concentrating it on one page, allowing you to a lesser extent an opportunity of positioning for competitive expressions with locales that are consolidating their connection value into a solitary report.
Having huge amounts of copied content makes your site seem as though it is jumbled with lower-quality (and perhaps manipulative) content according to search engines.
There are various things that can cause copy or slight content. These issues can be hard to analyze, yet you can see Webmaster Tools under Search Appearance > HTML Improvements to get a speedy finding.
What’s more, look at Google’s own breakdown on copy content. Many paid SEO tools likewise offer a method for finding copy content, like Moz Analytics and Screaming Frog SEO Spider.
5. XML Sitemap
XML sitemaps can assist Google and Bing with understanding your site and tracking down the entirety of its content. Simply be certain not to include pages that aren’t valuable, and know that presenting a page to a search motor in a sitemap doesn’t guarantee that the page will really rank for anything.
There are various free tools to generate XML sitemaps.
Track & Measure SEO Results
So once you begin composing your magnificent SEO content and kicking off these means, how would you really follow how well it’s functioning?
All over, this question has a genuinely direct response, with key SEO metrics to zero in on, yet with every measurement, there are a few vital factors to consider as you measure your site’s SEO performance.
1. Keyword Rankings
Taking a gander at where your site positions for a rundown of keywords unquestionably is certainly not the last destination, you can’t pay your staff in rankings, things like personalization in search results have made them variable across various locations, and therefore difficult to follow, and obviously, all they demonstrate is the place where you appear in search results. Some would even venture to such an extreme as to declare them dead.
Be that as it may, finding out about where your site positions for center terms can be a helpful leading mark of your site’s health. High rankings across a scope of keywords are a strong sign of organic search results.
This doesn’t mean you ought to get overly fixated on rankings for any one term.
Keep in mind: your definitive objective is to drive more pertinent traffic that drives more business, assuming you sell blue widgets, is it more critical that you rank for “blue widgets” or that you frame and execute an SEO strategy that assists you with selling more blue widgets in the most expense productive way imaginable? Use rankings as an overall health check, not a course-outlining KPI.
Various tools can assist you with really taking a look at your rankings. Most deal genuinely comparative functionality yet includes like nearby or mobile rankings are once in a while unique in a portion of the tools.
On the off chance that you’re a private venture or simply getting everything rolling with SEO, I’d prescribe picking a free and simple to-utilize device and watching out for a modest bunch of the center terms you need to track to assist you with checking progress.
2. Organic Traffic
Organic traffic is a greatly improved leading sign of the health of your SEO endeavors. By taking a gander at the organic traffic to your site, you can get a measure the genuine volume of guests coming to your site, and where they’re going.
You can quantify your organic traffic effectively with most analytics tools – since it’s free and the most utilized, we’ll take a gander at how to get this information in Google Analytics.
For a speedy check, you can basically take a gander at your site’s principle revealing page and click on “All Sessions” to channel for organic (traffic from search engines that exclude paid search traffic):
3. Organic Leads & Sales
This can be strong for locales by simply getting everything rolling with SEO in light of the fact that as often as possible the vast majority of your site’s traffic will be driven by what’s known as “branded inquiries,” or searches that contain your organization’s image name (for example a branded search for WordStream may be “WordStream PPC” versus a non-branded search term, which may be “pay-per-click software”).
You plainly need to have individuals searching for your image, and obviously, you believe them should track down you when they do, however except if your site has been punished by Google, you will in all likelihood rank for your image and have that branded traffic come to your site’s landing page.
What the greater part of your ongoing SEO endeavors ought to be revolved around is driving steady traffic to the site (individuals who probably won’t have found and drawn in with you otherwise).
As I mentioned in the catchphrase section of the guide, tragically, Google has made it challenging to get information around the genuine keywords individuals are searching for, yet by seeing page-level traffic (outside of your site’s landing page) you can begin to gather understanding into your generally SEO progress.
Taking a gander at rank information and utilizing the tactics mentioned in the catchphrase section of this guide will likewise assist you with getting more knowledge into the real terms that are driving traffic (and whether your SEO development is being driven by optimization endeavors rather than disconnected marketing).
Clearly, the essential method for estimating your search motor optimization results ought to be real leads, deals, income, and benefits. Like with any business activity you want to reply to: how does the action assist with moving your primary concern?
The least difficult way here is to lay out objectives or internet business following in an apparatus like Google Analytics.
You can utilize the above report to see organic traffic and objectives (or different internet business metrics) via the presentation page, and that implies that you are explicitly seeing who converts among individuals who are arriving on your webpage from an organic search (versus individuals who might have come to your website from PPC or another channel inside the window that your analytics following can follow, then searched for you, then converted).
This appears to be really direct, and by and large, for most organizations is a decent introductory method for estimating the progress of your SEO endeavors, yet once more there are a couple of provisos and things to remember with this information:
Online analytics is imperfect 100% of the time.
Assuming you’re transitioning from bulletins or newspaper ads to online marketing, you’ll probably be dazzled by the volume and precision of the information accessible, however, there can often be a variety of various following issues that can make the information you’re seeing anyplace from somewhat to stunningly off, consistently have a degree of doubt about information that doesn’t appear to add up and give your very best for having checks set up to ensure that your analytics information is synchronized to your real income and spend information.
Your framework could make holes in the following.
Assuming you have a back-end framework that you can’t exactly bind to analytics for reasons unknown, you could have a few holes between what you can follow as objectives and real deals.
Attribution and lifetime esteem metrics can be interesting. This is all the more a business and web metrics issue as opposed to something explicit to SEO, yet sorting out how you attribute deals to various channels and factoring in a lifetime’s worth of your webpage’s traffic can be interesting.
Ensure you’re applying similar kinds of extreme questions and endeavoring to gauge SEO the same way you would with some other marketing endeavor.



